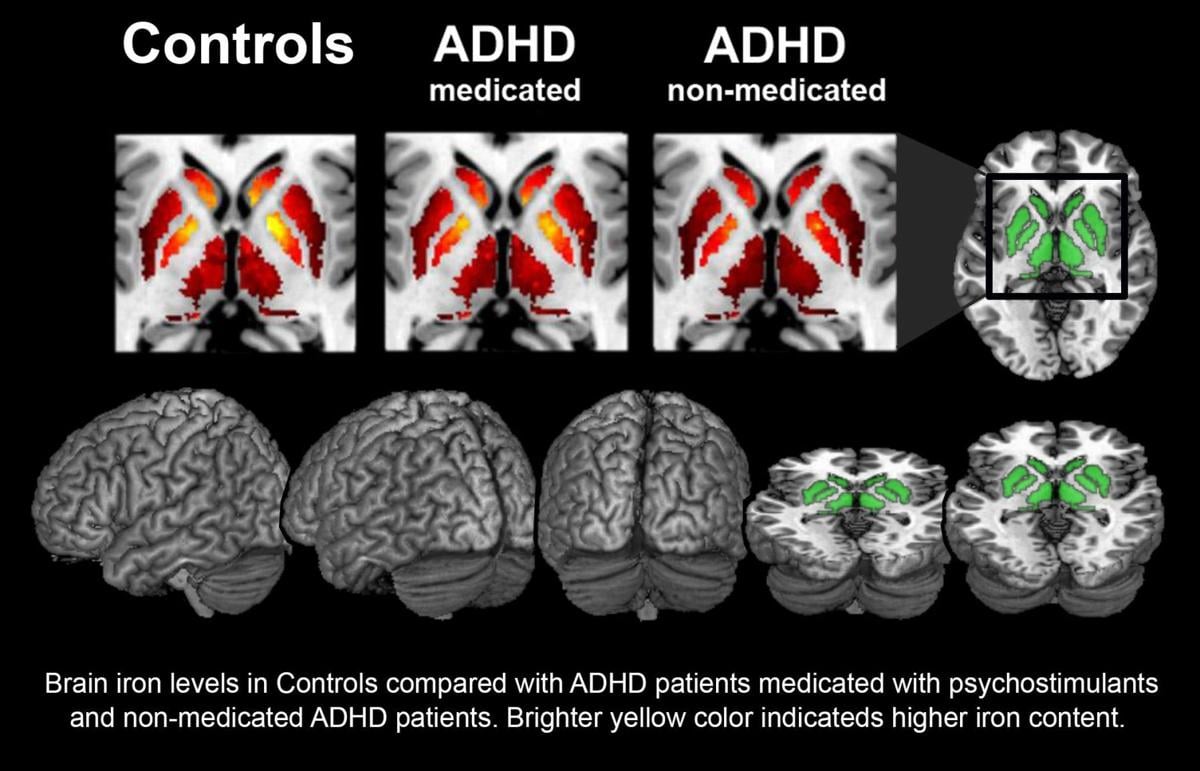
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) affects children and teens and can continue into adulthood. ADHD is the most commonly diagnosed mental disorder of children. Children with ADHD may be hyperactive and unable control their impulses. Or they may have trouble paying attention.
source:Webmd
Short Description:
- Is a neurodevelopmental disorder that occurs in childhood, and continues until adulthood and adulthood in different forms and symptoms.
- There are no clear and precise reasons why it occurs; however, there are some studies that have proven to be related to certain factors.
- Drug therapy is effective in controlling symptoms; however, its use does not dispense with behavioral and educational therapy.
- There is no analysis to diagnose the disorder; therefore, the diagnosis must be made by a specialist doctor.
- There are no ways to prevent it if there is more than one risk factor, but there are some ways that may reduce the incidence of infection.
Definition of disease:
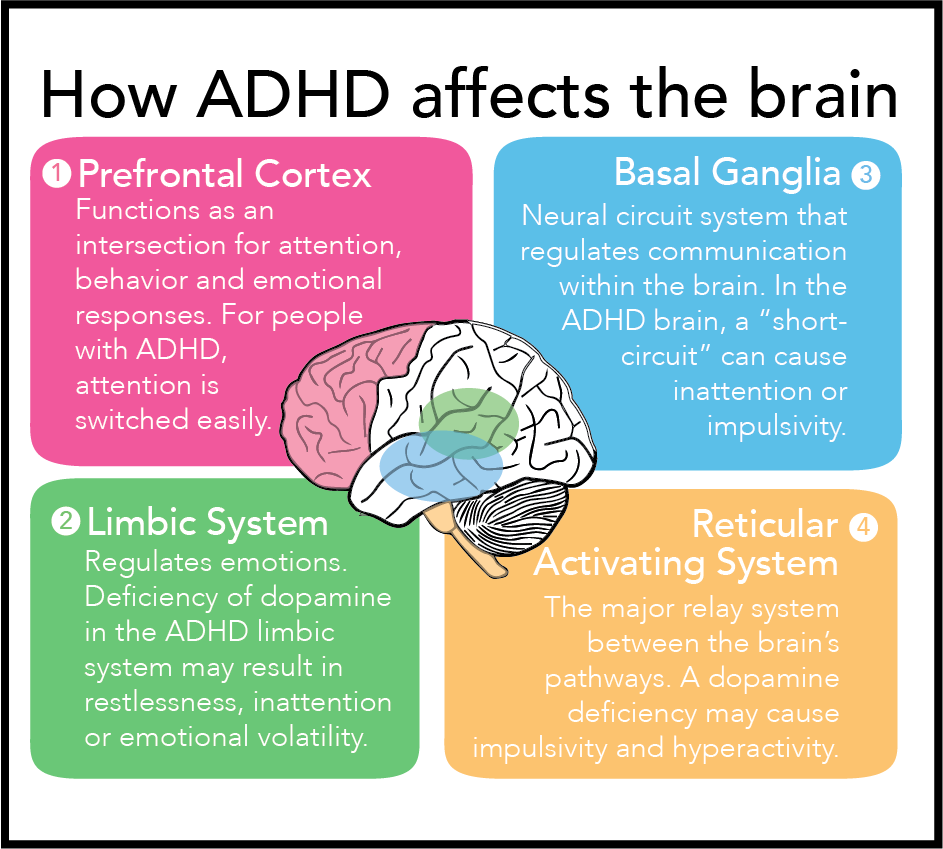
Is one of the neurodevelopmental disorders caused by a lack of chemical conductors (dopamine, noradrenaline) in the frontal cortex (the frontal lobe) that makes it easier for cells to carry out their work and communicate between the ends of the brain.
Other names of the disease:
AFTA - Attention deficit disorder with hyperactivity - Attention deficit and hyperactivity.
Types of disorder:
Some symptoms may increase, but this does not necessarily mean that there are no other symptoms. Symptoms may change at different ages (eg, hyperactivity and hyperactivity appear before school age and as soon as school enters, distractions begin to appear more clearly than others).
1 - distraction:
- They tend to have more distractions.
- Its percentage in females is higher than that of males.
2 - Hyperactivity and Impulsivity:
- They have symptoms of hyperactivity and hyperactivity.
- In males is higher than that of females.
3 - Common Type:
- Dispersion of attention involves hyperactivity and impulsivity.
- The most common type.
- They have all the symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder almost as much.
Associated Disorders:
Disorders that may occur in people with ADHD:
learning difficulties:
- Which make it more difficult to maintain order, accommodate, and respond to orders or requests of persons with particular disorders.
- Dyslexia and dyslexia are the most common learning difficulties among people with disorders.
Disruptive intractability disorder or interceptor challenge disorder:
- People with a lot of controversy, anger and nerve loss, refusal to follow the rules, blame others, deliberately annoy others.
- (Verbal or physical) with people or animals, lying, stealing, and escaping from school or home. For adults, they often behave in a legal way because of their violent temperament.
Mood disorders:
- Include depression, mania, and bipolar disorder.
- These disorders are characterized by severe mood changes. The child may continue to cry or worry for long periods that may last for days without any reason.
Anxiety disorders:
- People suffering from these disorders suffer from extreme anxiety about family, school or even professional matters.
- The disorder begins with a sense of stress and insomnia, and in severe cases, some may experience panic attacks.
Hyperactivity Disorder may appear in:
Autism spectrum.
Tourette syndrome.
Similar disorders:
Sleep disorders
Thyroid disorders
the reasons:
There are no clear and concise reasons for the cause of the disorder; however, some studies have shown that the disorder is associated with certain factors (eg family history, toxin exposure, injury during pregnancy, childbirth, or postpartum months).
Symptoms:
Dispersion and lack of attention:
- Lack of attention to detail and a lot of mistakes due to negligence.
- It is very difficult to maintain focus and attention.
- He does not seem to be listening to anyone talking to him.
- Ease of dispersion with any external influences.
- Difficult to follow instructions and instructions especially complex or serial.
- Difficulty in arranging or organizing.
- Dislike and avoid tasks that require constant mental effort and concentration.
- Loss of tools easily.
- Forget about everyday activities and tasks.
- Move from one activity or task to another without accomplishing either.
Hyperactivity:
- The difficulty of staying seated for a long time.
- Jogging and climbing a lot and anywhere (in children).
- Chat and talk a lot.
- Tampering with hands and feet like swinging while sitting on a chair.
- Difficulty participating in activities quietly.
- Bored quickly.
The impulse:
- Answer the questions before completing them, and not wait for the teacher to let him participate in the class.
- Difficult to wait for queues.
- Boycott others in conversation.
- Lack of thought and attention to the consequences or fear of things.
- Recklessness and participation in hazardous activities without hesitation.
- The inability to suppress what he wants to say regardless of who is talking to him.
Other :
- Chaos.
- Weak social relations and the difficulty of forming them.
- Weak self-confidence.
- Urgency.
- Love dazzling and draw attention.
- Lack of interest in cleanliness and appearance.
Although it is normal for a person to have some of these symptoms; however, suspicion begins with a disorder if:
- Very sharp.
- Often appear.
- Adversely affect their social life, their scholastic performance or their productivity at work.
When should I see a doctor?
- When symptoms appear in at least two different places (home, work, school).
- When it affects negatively and significantly in many aspects of his life (socially, professionally, educationally).
- When symptoms appear before the age of 12 years.
- When the symptoms persist for more than six months, and not be the result of emotional or emotional state or trauma.
Diagnosis :
There is no analysis of disorder diagnosis; therefore, a comprehensive assessment of the condition by a physician diagnoses the disorder by:
- Clinical examination; to exclude all other possibilities that may cause the same symptoms of the disorder.
- Collection of information: such as the sick and family history of the person, and matching the status information with diagnostic criteria.
- Anometer of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (Conner).
Risk factors:
- Genetics (most cases).
- Exposure to environmental toxins, such as high levels of lead, mercury, or chlorpyrifos, during pregnancy or at an early age.
- Low birth weight.
- Hypoxia.
- Smoking, alcohol, or drugs during pregnancy.
Complications :
- Deterioration of mental and mental health.
- Failure, poor academic performance, vocational and unemployment.
- To engage in legal problems or commit crimes.
- Frequent accidents in cars and others.
- Tension of social relations.
- Substance Abuse and Alcoholism.
- Suicide attempts.
Treatment :
The treatment of disorder depends on three basic pillars that complement each other:
- Drug therapy:
Helps to increase focus and attention for longer, reduce movement and impulse, and divided drugs used to two types:
- Active drugs:
It activates neurotransmitters, thus increasing the ability to concentrate and control behaviors.
- Non - stimulant drugs (inhibitory).
It works to strengthen chemical receptors in brain cells and increase the effectiveness of neurotransmitters to improve concentration.
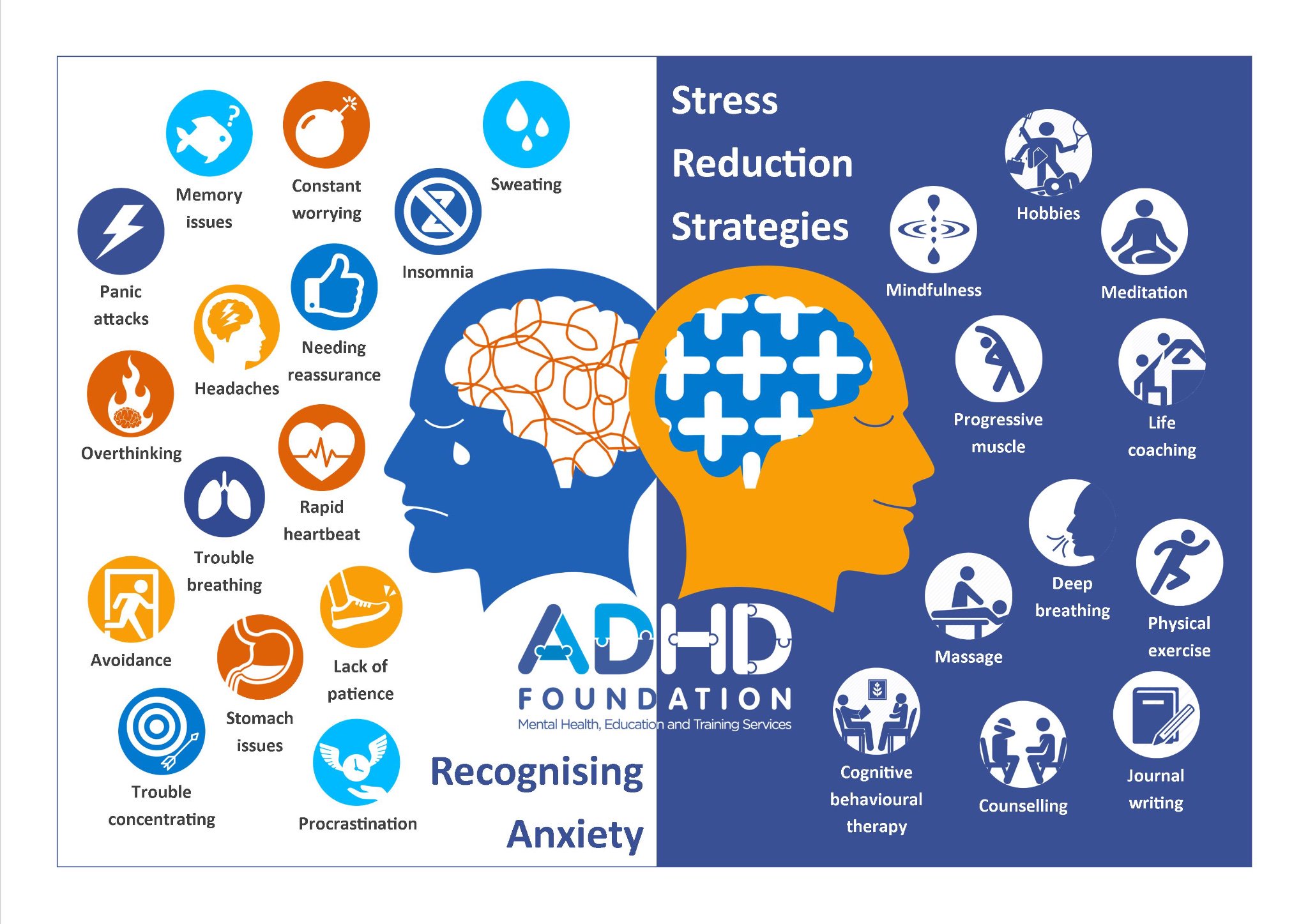
Managing stress & anxiety for children during exams - a useful infographic for schools & parentsSource ADHD Foundation
- Behavioral and educational therapy:
This treatment depends on modifying the child's behavior through methods and strategies used by the parents; to replace his positive negative behaviors and train him to acquire new skills.
Drug therapy is effective in controlling symptoms of major disorder; however, its use alone does not dispense with complementary behavioral and educational therapy.
protection:
Although it is difficult to prevent (almost impossible if more than one risk factor is available), there are some ways in which it may be reduced; but there are no sufficient studies to prove its effectiveness:
- Protect the child during pregnancy or in the first years of his life from exposure to any environmental contaminants such as lead (paint the walls containing), mercury and insecticides.
- Avoid smoking especially during pregnancy (for both mother and father) or even in places where there are many smokers.
common questions:
- Does the disorder disappear after puberty?
Symptoms of the disorder may not be obvious in adults; they may be less hyperactive; but they may continue to have impulse and distraction.
Can it be detected during pre-marital screening?
Can not be detected; because the gene or chromosome causing it is unknown.
wrong concepts:
- Turbulence is just an excuse for parents to pamper their children and make it impossible for their misbehavior.
In fact, there are children who do not show symptoms of the disorder despite receiving the same treatment, and there are research studies on the status of adopted children. However, one of the biological parents is disturbed, and despite their upbringing and presence with non-infected parents, the symptoms have appeared.
The causes of the disorder are: poor education, emotional trauma, addiction to electronic devices and video games, watching television for hours, lack of physical activity, food sensitivity, eating sugars and additives.
The fact is that the disorder is a neurological disorder caused by a chemical imbalance in the neurotransmitters that may be caused by a genetically modified organism. However, poor parenting, or parental neglect of the child, addiction to video games, etc., may exacerbate but not cause symptoms of the disorder.
Antihypertensive drugs cause addiction.
Fact: Energetic drugs are relatively safe and do not cause addiction.
Not : let me know if there are any mistakes Contact









0 Comments