
A telescope is a device that collects light from distant celestial bodies to form a close-up image. All telescopes are characterized by their possession of the so-called objective lens which determines the type of telescope.
Humans dwell throughout this earth in the sky, wondering what things they see there at the top. A long time ago, the sun and the moon returned mysterious objects that could be seen in the morning and evening, but the planets were more ambiguous; because of their extreme distance, we can only see bright spots, unlike the things we can see on the ground, , Listening to them, tattooing them, and tasting them.
Sky watchers have long relied on one way to learn more about space, through their eyes and imagination, but recently, in the history of humanity, astronomers have been able to expand our vision and imagination. Galileo led the exploration of modern space at the beginning of the 17th century, using a device specially made for navigation missions to discover the sky. The instrument used at the time was telescopes, a machine used to collect and concentrate light.
Our atmosphere does not allow most electromagnetic radiation access to the Earth, and allows the corresponding passage of visible light, parts of the radio beam, and small parts of the infrared and ultraviolet parts. Our eyes can detect the visual package. So all the modern telescopes have been created to monitor this part of the electromagnetic spectrum. This was the case until the 1940s, when astronomers began to monitor another part of the electromagnetic spectrum, the radio beam.
The development of space technology has enabled astronomers to place telescopes outside the Earth's atmosphere and to discover all the places there by using the full spectrum of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Types of telescopes
There are two basic types of telescopes: reflectors (Reflectors), and refractors (Refractors), called the telescope that collects light with part (objective lens - Objective), which you select the telescope type, as using the telescope Alkasir glass lens to represent the objective lens has, placed The glass lens is at the top of the telescope, causing the refraction of light to pass through it. The reflective telescope uses a glass mirror to represent its objective lens. The mirror is placed at the end of the telescope and causes a reflection of light when it collides.
Telescopic telescopes
The telescope uses a lens to collect and concentrate light. The first telescope was made of kasir, and the small telescopes sold in the stores are of the kasir type, in addition to the distance used in the rifles.
Characteristics of the telescope:
1. The telescope is solid. After the initial alignment, its optical system is more resistant to shocks than the reflective telescope.
2. The glass inside the telescope tube is insulated from the air; therefore it does not need to be cleaned always.
3. As a result of the tube being closed from the outside, the effect of the air currents and the effects of temperature change is excluded. This means that the image in the kasir is more stable and clear than the equivalent reflective telescopes in size.
Although excellent telescopic telescopes are still being manufactured, their faults have stood in the way of building very large telescopic telescopes for use in astronomical explorations.
Disadvantages of the alkaline telescope
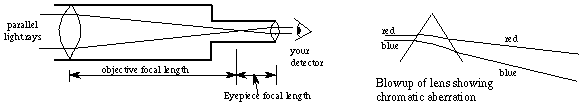
1. All telescopic telescopes suffer from chromatic aberration, which is the deviation or dispersion of light. This phenomenon produces a rainbow of colors around the image, and long wavelengths (red) deviate less than the shorter wavelengths (blue) Through the passage of the lens; due to the wave nature of light.
This method is used in prisms to produce a beautiful rainbow, but can this spoil the picture ?! There are several ways to reduce chromatism, one using a number of corrected lenses to counter this aberration, and the other using a very long focal distance - the distance between the focus and the objective lens - to reduce this effect, so the old telescopes are made too long.
● The quality of light passing through the lens depends on the nature of the wavelength. Ultraviolet light does not pass through the lens at all.
● The quality of the light crossing decreases as the thickness of the lens increases.
● It is difficult to make a glass lens without defects inside the lens, with a perfect bend on either side of the lens.
● The objective lens can only be reinforced at the end, and the glass lens will bend under its actual weight.
Because of these defects, the largest telescope is built in the Yerkes Observatory. It has a 1.02-meter (40-inch) optical lens at one end and a 19.2-meter (63-foot) tube.
The two images below show the largest telescopes in size. The first image shows the astronaut Kyle Cudworth standing next to the objective lens to give you an idea of the size of the telescope. In the second image, the 40-inch (40-inch) telescope is shown at the Yarkas Observatory.
The third image shows Edward Emerson Bernard EEBernard standing at the 36-inch Lick-Lick lens. The final image of the 0.91-meter (36-inch) calcareous telescope at the Lick Observatory is observed by the astronaut at the bottom left of the image.
Reflective telescopes
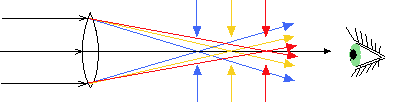
The reflective telescope uses the mirror to collect and focus the light. All the celestial objects, including those in our solar system, are so far away that all the light rays coming from them reach Earth in the form of parallel rays because the light rays are parallel to each other, This mirror, in this way, concentrates the parallel rays at one point, and the research telescopes and the large amateur telescopes are all of the reflective type, superior to the telescopic telescopes.
Advantages:
1. Reflective telescopes do not have a ziga color, because all wavelengths are mirrored in the same way.
2. The objective mirror is reinforced along the back side of the telescope, so it is possible to make these telescopes at a very large size.
3. Reflective telescopes are less expensive to make than the same size telescope.
4. There is one ideal aspect of the objective mirror of the reflective telescope, which is because of the reflection of the light from the mirror object, not through it.
The positives of reflective telescopes did not prevent astronomers from dealing with some of the disadvantages.
Disadvantages of reflective telescopes:
1. Easy to set optical system out of alignment.
2. The telescope inverter tube is open on the outside, and the optical parts of the telescope need constant cleaning.
3. The secondary mirror is often used to redirect light at a more comfortable point of view, which, together with its supporting parts, can produce curvature effects. Illuminating objects have protrusions called (the Christmas Star effect).










0 Comments