You may not realize the risk of cancer when you drink wine, beer, or alcohol. In fact, 7 in 10 Americans are unaware of the link. Studies have found that drinking alcohol causes chemical and physical changes in our bodies, which in turn raises the incidence of cancer and is directly responsible for about 5% of new cancers and related deaths around the world.
Alcohol and Cancer:
In general, the higher your consumption, the greater the risk of cancer. Alcohol drinkers who consume two to three drinks per day have a higher risk of cancer and death due to alcohol. Even if you consume low amounts of alcohol (three drinks a week max), you still have a higher chance of not drinking alcohol.
Alcohol raises the chance of cancer in seven parts of your body, including:
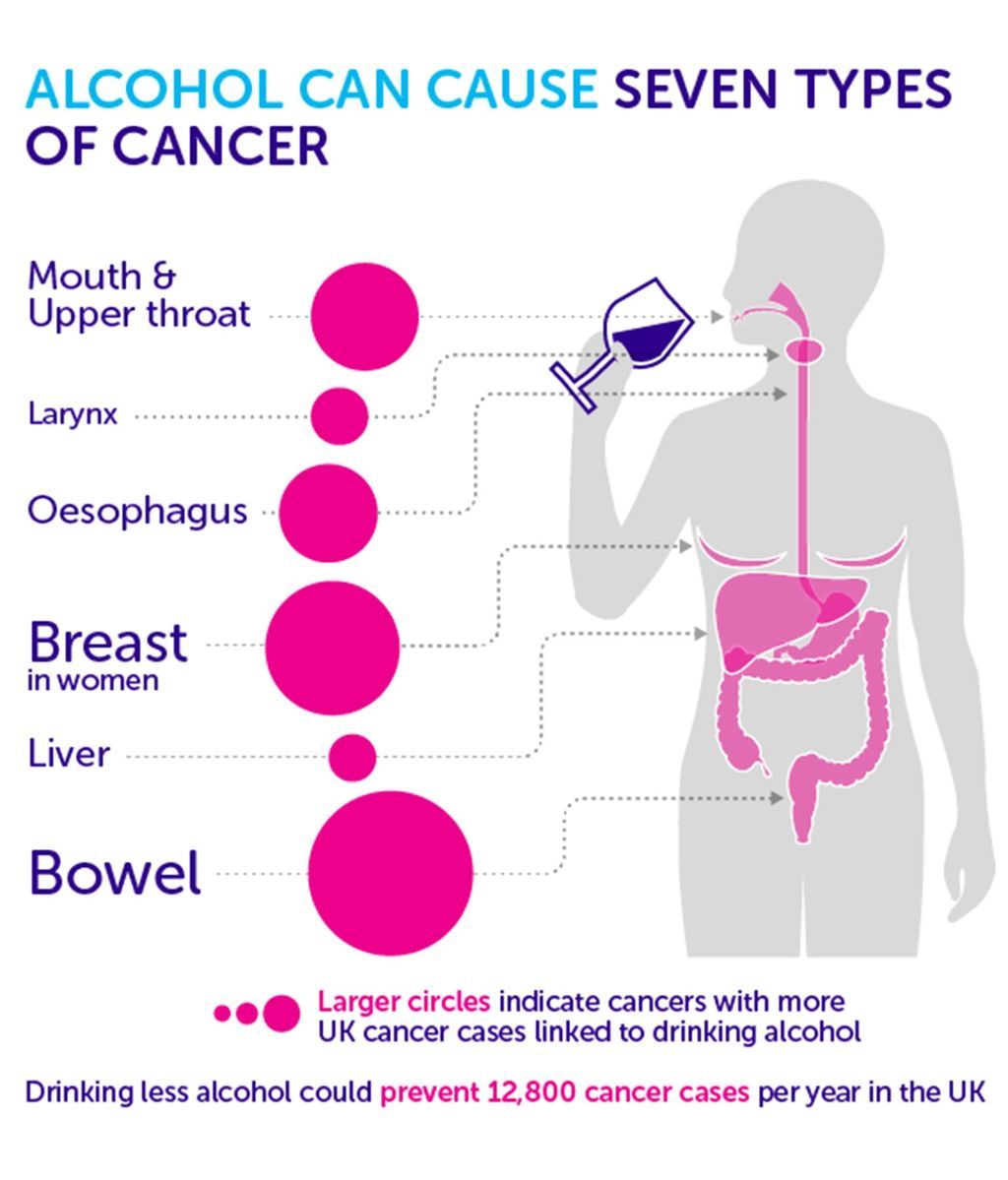
: Types of cancers caused by drinking alcohol
Liver
The basic liver function is the filtering of blood and toxins. Alcohol is a toxic substance of the liver cell, and its excessive consumption can cause irritation and scarring of the liver. Excessive amounts can also increase the risk of liver cancer compared to the risk of infection if not consumed.
Mouth and throat
We have some of the strongest evidence of this, having an overactive drink alcohol has a fivefold higher likelihood of injury than those who do not consume alcohol because alcohol harms the cells in these tissues. Even the risk increases if you light your cigarette. Alcohol paves the way for harmful chemicals in tobacco to enter the cells.
esophagus
The risk of esophageal cancer - which can be aggressive and deadly - increases with the increase in the number of drinks, and alcohol increases the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma in particular, a type of cancer that affects the lining of the esophagus.
Colon and rectum
Men who drink more often with colon or rectal cancer are more likely than women who drink heavily. In general, those who drink more alcohol than both sexes are 44 percent more likely to be infected than those who do not.
Breast
Women are more likely to have breast cancer with the weekly intake of alcohol. Why can alcohol be harmful?
Alcohol enters the cells easily and can cause damage to cell DNA and triggers multiple changes in the body:
- Chemical toxins: When the body breaks down ethanol in alcohol, it releases chemical toxins thought to cause cancer.
- DNA mutations: Alcohol stimulates the organs and tissues of the body. When the body tries to repair itself, DNA errors can occur, allowing cancer cells to grow.
- Hormones: Alcohol raises the level of estrogen in women's bodies, which can support cancer growth.
- Nutrients: Alcohol reduces the body's ability to absorb essential vitamins and other nutrients that may affect the risk of cancer. These include folate, vitamin A and b.
- Weight gain: Alcohol builds up a lot of calories, and overweight and obesity are associated with many types of cancers.
What is the amount that is considered redundant?
When it comes to cancer, your drink does not seem to matter. It is not clear whether taking off or reducing alcohol reduces the risk of cancer.
But the biggest risk is when the amount of four drinks exceeds a day, and 42.5 grams of wine, 141.75 grams of wine or 340.2 grams of beer are counted as one drink. Alcohol is limited to one drink per day for women and one drink a day for men. You may think you do not drink too much, but the drink in your cup may contain more alcohol than you think. Some drinks may contain several doses of alcohol, and alcohol concentration in excellent beer is the same as in barley.
Source :webmd








0 Comments