
Alzheimer's disease is a neurological disorder that causes brain cell death, memory loss and decreased cognition. Alzheimer's is the most common mental illness, accounting for nearly 80% of cases in the United States.
In 2013, 6.8 million patients in the United States reported that they had a mental illness, including 5 million people who had Alzheimer's disease. By 2050, figures are expected to double. Alzheimer's is a neurological disease. Initially, the symptoms are moderate, but they become severe over time.
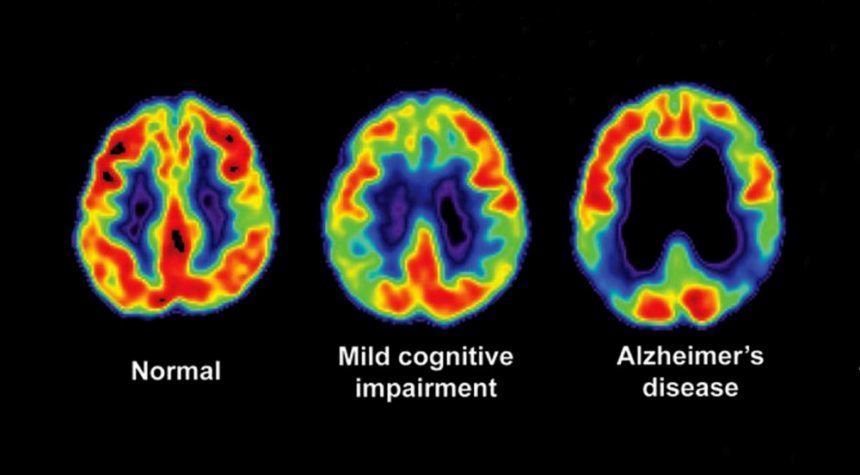
The brain of a person with Alzheimer's compared to the brain of a healthy person
Quick facts about Alzheimer's disease:
Alzheimer's disease is the most common mental illness. Occurs when the plate contains amyloid beta in the brain. When the symptoms worsen, it becomes difficult for the patient to remember new events, to understand, to identify people he knows. The person with Alzheimer's needs help all the time.
For Alzheimer's disease, the patient should experience lower cognitive or behavioral functions and performance than before. This decline should be inconsistent with their ability to work in their normal jobs or activities.
This low perception should be seen at least in two of the five symptoms listed below:
Low ability to accept or recall new information, which may lead - for example - to:
- Frequently asked questions or conversations.
- Put personal things in place.
- Forgetting occasions or appointments.
- Lost in a familiar way.
Weak logic, complex tasks, and sentencing, for example:
- Poor understanding of safety hazards.
- Inability to manage conditions.
- Weak decision-making capacity.
- The inability to plan sequential or complex activities.
Weakness of sight, which is not, for example, due to the problems of the eyes. These may be:
- The inability to distinguish recognizable faces or objects or to find things that appear directly.
- Inability to use simple tools, for example, wear clothes.
- Weakness of the ability to talk, read, and write, for example:
- Difficult to think of well-known words during conversation, hesitation.
- Errors in speech, spelling, and writing.
Changes in personality and behavior, for example:
Mood changes away from personality, including frenzy and indifference, social disconnection or scarcity of interest, motivation, or initiative.
Loss of emotion.
Loss of emotion.
Person who is not resistant, obsessive, or socially unacceptable.
If the number of symptoms and seriousness of the existence of mental imbalance, the following factors can confirm the incidence of Alzheimer's:
- Gradually, from months to years, rather than hours or days.
- Significant deterioration of the level of natural knowledge of the individual in specific areas.
If symptoms begin or worsen within hours or days, urgent health care should be requested, and this may indicate serious illness.
Alzheimer's is most likely when memory loss is prominent, especially in the learning area and retrieving new information.
Language problems may also be early symptoms, for example, suffering to find the right words. If the vision deficit is more pronounced, the following will occur:
- Inability to distinguish objects and faces.
- Difficult to recognize separate parts of a scene at once.
- Difficulty reading texts, known as blindness reading.
The most prominent deficit in executive dysfunction is logical, judgmental, and problem solving.
Other early signs:
In 2016, the researchers published research findings suggesting that changing humor may be an early indicator of Alzheimer's. NEW YORK (Reuters Health) - Alzheimer's features, such as brain damage, may be present in the middle of life, but symptoms do not appear until years later, a new study suggests.
Early onset of Alzheimer's disease:
The early onset of Alzheimer's disease affects people at an early age who have a family history of the disease, practically between 30 and 60 years of age. Less than 5% of cases of Alzheimer's disease.
Stages of Alzheimers:
Alzheimer's exacerbation can be stopped in three basic stages:
- Pre-clinical stage, ie before the onset of symptoms.
- Moderate weakness in perception, when symptoms are moderate.
- Mental illness.
In addition, the Alzheimer's Association describes 7 stages of low cognitive perception, depending on the severity of the symptoms. The scale of disease ranges from morbidity to moderate and non-strong decline, eventually leading to "very severe deterioration". Diagnosis is not usually clear until the fourth stage, described as "an early-stage Alzheimer's disease."
Alzheimer's and mental illness:
Mental illness is a comprehensive term for a range of situations that include loss of perception. Alzheimer's is the most common type of mental illness. Includes forming the plates and holding the brain. Symptoms begin gradually and include decreased cognitive function and speech ability. There are other types of mental illness such as Hannington's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Crockfield's Jakob disease. You can get more than one type of mental illness.
Diagnosis:
There is no single test for Alzheimer's disease, so doctors cast a look at the symptoms and evidence, taking the patient's medical history, excluding other cases before making the diagnosis.
Doctors may also check neurological function, for example, checking balance, senses, and reactions. Other assessments may include blood and urine tests, CT scans or MRI of the brain, and depression screening.
Symptoms of mental illness are sometimes linked to genetic disorders such as Huntington's disease, so genetic testing is performed.
After excluding other potential cases, the doctor conducts memory and cognitive tests, to assess a person's ability to think and remember.
Doctors may also check neurological function, for example, checking balance, senses, and reactions. Other assessments may include blood and urine tests, CT scans or MRI of the brain, and depression screening.
Symptoms of mental illness are sometimes linked to genetic disorders such as Huntington's disease, so genetic testing is performed.
After excluding other potential cases, the doctor conducts memory and cognitive tests, to assess a person's ability to think and remember.

Cognitive assessment:
To confirm the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease, the following elements must be sufficiently strong to affect daily activities:
- Gradual loss of memory.
- Gradual deterioration of perception.
- The questions that you may ask in the cognitive capacity check include the following:
- how old are you?
- How long, for the nearest hour?
- In which year are we?
- What is the name of the hospital or city where we are located?
- Can you distinguish two people, for example, your doctor, nurse, or caregiver?
- what's your birthday?
- In what year did he get (a very well known historical event)?
- Cm president.
- Count down from 20 to 1.
- Set the address at the end of the test I will give you now (eg, "42 West Street").
- A number of evaluation tools are available to assess cognitive function.
Genetic testing:
In some cases, genetic testing is appropriate. The gene known as APOE-e4 is associated with higher rates of change for people over the age of 55, thus developing the condition for Alzheimer's. Early screening may indicate the risk of infection or progression of the disease to individuals. However, this examination is controversial, and the results are not fully reliable. In the future, emerging biological tests may make it possible to assess vital indicators of people at risk of developing Alzheimer's disease.
the cure:
There is no known cure for Alzheimer's, since the death of brain cells can not be stopped. However, there are therapeutic interventions that make it easier for people to live with the disease. According to the Alzheimer's Association, the following include important elements for mental illness:
- Effective management of any symptom or condition that occurs in conjunction with Alzheimer's.
- Daily care activities and programs.
- Engage support groups and services.
Pharmacotherapy:
Medications for moderate diseases are not available for Alzheimer's disease, but may reduce some of the symptoms and help improve the quality of life.
Choline inhibitors approved in the United States for casual ambulances include:
Choline inhibitors approved in the United States for casual ambulances include:
- Donbizle
- Revastigmone
- Eccelon
- Another type of drug, including naminda, NMDA receptor receptor, can also be used alone or in combination with choline inhibitor.
Treatment of another type:
The need for a good quality of health care becomes more important when the individual's ability to live independently is reduced.
The results of a study in rats, published in the journal Nature, suggested in 2016 that memories of people with Alzheimer's can be re-stored in early cases.
The results of a study in rats, published in the journal Nature, suggested in 2016 that memories of people with Alzheimer's can be re-stored in early cases.
Causes of Alzheimer's and Risk Factors:
Like all types of mental illness, Alzheimer's occurs because of the death of brain cells. Is a disease caused by non-renewal of nerve cells, this means that there is a gradual death of brain cells occurs over time. The person with Alzheimer's has very few neurons and connections.
Anatomy showed that the nervous tissue in the brain of an individual with Alzheimer's had small layers, known as platelets and nodes, that formed over the tissue.
Platelets were found between dead brain cells, made of a protein known as beta amyloid. The nodes are formed inside neurons, which are made from another type of protein, called Tau. Researchers did not fully understand why these changes occurred. There are many different factors involved.
The Alzheimer's Association published a 16-page journal of what happens during the development of Alzheimer's disease.
Risk factors for Alzheimer's disease:
Risk factors for the development of an unavoidable situation include:
- Aging.
- Family History of Alzheimer 's Disease.
- Download some genes.
Some modifiable factors that help improve the situation include:
- Exercise regularly.
- Maintain the health of the vascular system.
- Risk management of vascular disease, diabetes, obesity, smoking, high blood pressure.
- Follow a varied and healthy diet.
- Participate in long-term learning and cognitive training.
Some studies suggest that staying mentally and socially active may reduce the risk of Alzheimer's disease. Factors that increase risk include:
- Exposure to severe or recurrent brain injury.
- Exposure to some environmental pollutants, such as toxic metals, pesticides and industrial chemicals.
To reduce the risk of TBI associated with mental illness, it is always important to wear a seat belt when traveling by car, take precautions when exercising, and follow health instructions and instructions to ensure adequate rest and healing if an injury occurs. Moderate TBI appears to double the risk of Alzheimer's disease, while acute TBI increases the condition by 4.5 times.








0 Comments